SIP ALG and VoIP: What It Is and Why Businesses Should Disable It
SIP ALG (Session Initiation Protocol Application Layer Gateway) is a router feature that modifies VoIP packets, often causing more problems than it solves for modern business phone systems.
- SIP ALG can cause dropped calls, one-way audio, and failed registrations in VoIP setups.
- Disabling SIP ALG resolves most common VoIP call quality issues instantly.
- Modern VoIP systems use advanced NAT traversal that makes SIP ALG unnecessary and harmful.
Disable SIP ALG on your router and configure proper QoS settings for optimal VoIP performance.
Business phone systems have evolved over the past decade, with VoIP technology transforming how companies communicate. However, many organizations experience frustrating call quality issues that seem to appear without warning. About 45% of VoIP users experience packet loss during calls, impacting voice clarity and business operations. While multiple factors can cause VoIP problems, one of the most common culprits hiding in business networks is a router feature called SIP ALG.
SIP ALG is one of those well-intentioned technologies that often creates more problems than it solves. Originally designed to help older VoIP systems navigate network firewalls, this router feature has become a primary source of call quality issues for modern business phone systems. Understanding why and how to disable SIP ALG for VoIP can resolve many persistent call problems that plague business communications.
What Is SIP ALG and How Does It Work?
SIP ALG stands for Session Initiation Protocol Application Layer Gateway. This technology operates as part of your router’s firewall system, designed to inspect and modify SIP packets as they travel through your network. To understand why this becomes problematic, you need to grasp the basic components involved.
Session Initiation Protocol is the underlying technology that powers most VoIP phone systems, managing device registration, call setup, and session termination. Application Layer Gateway functions as a network address translation tool that attempts to rewrite packet headers, changing private IP addresses to public ones as data passes through your router.
The original purpose of SIP ALG made sense for legacy phone systems that struggled with Network Address Translation environments. Early VoIP implementations lacked sophisticated NAT traversal capabilities, so routers attempted to help by modifying packet headers. However, modern VoIP systems have evolved beyond these limitations, incorporating advanced protocols like STUN, TURN, and ICE that handle NAT traversal elegantly without router intervention.
When SIP ALG operates on your network, it examines every SIP packet traveling through your router, analyzing the Session Description Protocol payload and modifying IP address information. This process occurs automatically and often without any visible indication that packet manipulation is taking place.
Why Does SIP ALG Cause Problems for Modern VoIP Systems?
Modern business phone systems operate with sophisticated protocols designed to handle the complexities of internet-based calling. When SIP ALG attempts to “help” by modifying these carefully crafted packets, it often corrupts critical information that VoIP systems depend on for proper operation.
The packet rewriting process is the core problem with SIP ALG functionality. When your router modifies SIP headers and SDP content, it changes essential addressing information that VoIP servers use to route calls correctly. This modification can break the delicate negotiation process that occurs when establishing voice connections, leading to failed call attempts and poor audio quality.
Header tampering creates particularly serious issues for encrypted VoIP traffic. Many modern business phone systems use Transport Layer Security for signaling and Secure Real-time Transport Protocol for media transmission. SIP ALG cannot properly handle these encrypted communications, often corrupting packets in ways that make them unreadable by destination servers.
Network Address Translation conflicts are another reason to disable SIP ALG for VoIP systems. Modern phone setups expect to handle NAT traversal through built-in protocols, but SIP ALG interference can confuse these mechanisms. This confusion often results in situations where VoIP servers cannot properly identify devices behind firewalls, leading to registration failures and call routing problems.
How SIP ALG Affects Business VoIP Calls
When call quality problems disrupt business communications, they create measurable costs through lost productivity, missed opportunities, and damaged customer relationships. A quarter of VoIP users cite call quality issues as their primary service dissatisfaction, highlighting the impact these problems have on business operations.
Registration and Connection Failures
Failed registrations are one of the most common SIP ALG-related problems affecting business phone systems. When devices cannot properly register with VoIP servers, employees lose the ability to make and receive calls through their assigned extensions. This registration failure occurs because SIP ALG modifies the contact headers in registration requests, providing servers with incorrect addressing information.
Intermittent connectivity issues plague many businesses using routers with active SIP ALG. Phones may work correctly for hours or days then suddenly lose registration or experience call failures. This unpredictable behavior makes troubleshooting difficult and creates uncertainty about communication reliability.
Audio Quality Issues
One-way audio is a frustrating SIP ALG-related issue for business users. This problem occurs when one party can hear the other clearly but the return audio fails to reach its destination. SIP ALG modification of media negotiation parameters often causes servers to incorrectly route return audio paths, creating this asymmetric audio situation.
Choppy or broken audio quality results from packet timing issues introduced by ALG processing. Real-time voice communications require consistent packet delivery timing, and any irregularities create audible distortions. When routers spend varying amounts of time processing different packets, it introduces jitter that manifests as choppy audio quality.
Call Management Features
Hold and transfer functions frequently fail when SIP ALG interferes with session management signaling. These advanced call features require precise coordination between VoIP devices and servers, exchanging specific control messages that enable features like putting calls on hold or transferring them to other extensions. SIP ALG modification of these control messages often breaks the feature coordination process.
Conference calling may also be affected by SIP ALG interference. Multi-party calls require complex media mixing and session management that can be disrupted when routers modify the signaling information that coordinates these functions.
How to Disable SIP ALG for VoIP on Common Routers
Disabling SIP ALG requires accessing your router’s administrative interface and locating the appropriate settings. The exact process varies between router manufacturers and models, but following these steps ensures successful configuration regardless of your specific hardware.
Preparation Steps
Before making any router configuration changes, document your current settings by taking screenshots of existing configurations. This documentation proves invaluable if you need to reverse changes or troubleshoot unexpected issues. Additionally, ensure you have administrative credentials and schedule the change during a maintenance window when a temporary communication disruption won’t impact business operations.
Contact your IT department or network administrator before proceeding if you work in a larger organization. Many businesses have specific network policies and change management procedures that must be followed when modifying SIP ALG router settings.
Router-Specific Instructions
Cisco and Linksys routers typically place SIP ALG settings under the advanced firewall or NAT configuration menus. Access the router’s web interface, go to Advanced Settings, then look for sections labeled “Firewall,” “NAT,” or “Application Layer Gateway.” Uncheck any options related to SIP inspection or SIP helper functions, then save your configuration changes.
Netgear routers often place SIP ALG controls in the Dynamic DNS or Port Forwarding sections of their administrative interface. Look for checkboxes labeled “Disable SIP ALG” or “SIP Transformations” and ensure these options are disabled. Some Netgear models require navigating to Advanced > Setup > WAN Setup to locate these settings.
TP-Link devices group SIP ALG with other application-specific gateway controls. Check under Advanced > NAT Forwarding > ALG for SIP-related options, or look in the Security > Firewall section for application layer gateway settings. Disable any SIP-related entries and apply the changes.
Fortinet FortiGate firewalls require command-line interface access to completely disable SIP ALG for VoIP. Use the commands “config system settings,” followed by “set sip-expectation disable” and “set sip-nat-trace disable” to properly disable SIP inspection features.
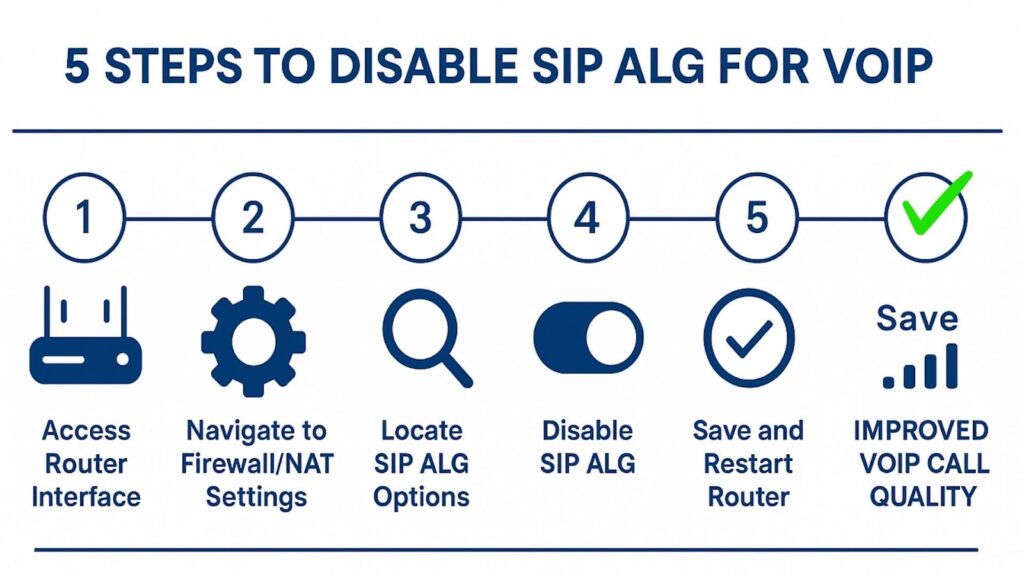
Verification and Testing
After disabling SIP ALG, restart your router to ensure that all changes take effect. Wait several minutes after the restart before testing VoIP functionality to allow all systems to re-establish connections.
Test your VoIP system thoroughly after making changes. Make test calls between internal extensions and to external numbers, verifying that both audio directions work correctly. Check advanced features like hold, transfer, and conference calling to ensure that all functionality operates as expected.
7 Essential VoIP Troubleshooting Tips Beyond SIP ALG
Resolving SIP ALG issues is just one component of comprehensive VoIP optimization. These essential VoIP troubleshooting tips address the most common network-related problems that affect business phone system performance.
- Configure Quality of Service Settings Properly: Quality of Service configuration ensures that voice traffic receives network priority over less time-sensitive data transfers. Access your router’s QoS settings and create rules that prioritize traffic on UDP ports 5060 (SIP signaling) and your RTP media port range. Set voice traffic to the highest priority level available.
- Open Required Firewall Ports: Voice traffic requires specific network ports to function correctly. Configure your firewall to allow UDP traffic on port 5060 for SIP signaling and the RTP port range specified by your provider, typically 10,000–20,000.
- Monitor Network Bandwidth Utilization: Each concurrent call requires approximately 85–100 kbps of bandwidth, depending on the codec used. Calculate your maximum concurrent call requirements and verify that your internet connection provides sufficient capacity with reasonable overhead.
- Update Router Firmware Regularly: Router manufacturers frequently release firmware updates that address VoIP compatibility issues and security vulnerabilities. Check your router manufacturer’s website quarterly for firmware updates and apply them during scheduled maintenance windows.
- Implement Network Segmentation: Separate voice traffic from data traffic using VLANs or dedicated network segments when possible. This separation prevents data-intensive applications from competing with voice traffic for network resources.
- Test Network Performance Regularly: Use network monitoring tools to test latency, jitter, and packet loss on a regular schedule. Establish baseline performance measurements and monitor for degradation that might indicate developing network problems.
- Coordinate with Your SIP Provider: Maintain regular communication with your VoIP service provider regarding network optimization and troubleshooting procedures. Many providers offer specific configuration recommendations for popular router models.
Network Optimization Best Practices
Optimizing your network for VoIP involves more than disabling problematic features. Comprehensive network optimization ensures reliable voice communications and minimizes the likelihood of future call quality issues.
Internet Connection Requirements
Business VoIP systems require stable, high-quality internet connections with sufficient bandwidth for peak usage periods. Understanding SIP trunk capacity requirements helps determine appropriate bandwidth allocation based on maximum concurrent calls multiplied by approximately 100 kbps per call. Add 20% more for network protocol overhead and burst capacity.
Latency requirements for quality voice communications mandate round-trip times under 150 milliseconds to prevent noticeable conversation delays. Test your internet connection’s latency to major destinations and work with your ISP to optimize routing if excessive delays impact call quality.
Router and Network Hardware Considerations
Business-grade routers provide more sophisticated traffic management and QoS capabilities compared to consumer-grade equipment. When selecting network hardware for VoIP deployment, prioritize devices that offer granular traffic control, advanced firewall features, and robust quality of service implementations.
Session Border Controllers can provide additional VoIP optimization by handling NAT traversal, security filtering, and media optimization functions. These specialized devices integrate between your internal network and internet connection, providing professional-grade VoIP support.
Security Considerations When Disabling SIP ALG
Disabling SIP ALG affects your network’s security, requiring careful consideration of alternative protection measures. While modern VoIP systems handle NAT traversal more securely than SIP ALG modification, businesses must implement appropriate security controls to protect voice communications.
Firewall Configuration for VoIP Security
Properly configured firewalls provide VoIP security without the problematic packet modification that characterizes SIP ALG operation. Create specific firewall rules that allow required VoIP traffic while blocking unauthorized access attempts. Implement connection state tracking to ensure that return traffic matches legitimate outbound connections.
Regular security monitoring helps detect unauthorized VoIP usage or system compromises that could result in toll fraud or data breaches. The VoIP market is projected to reach $326.27 billion by 2032, making VoIP systems increasingly attractive targets for cybercriminals.
Alternative Network Protection Methods
Session Border Controllers provide comprehensive VoIP security features, including user authentication, call authorization, and media encryption. These devices offer professional-grade protection that surpasses basic router-based security while maintaining compatibility with modern VoIP protocols and encryption standards.
Regular security audits ensure that your VoIP security measures remain effective against evolving threats. IBM’s Cost of a Data Breach Report found that the global average cost reached $4.4 million, highlighting the importance of robust security measures for all business communications systems.
How to Prevent Future VoIP Issues
Proactive network management prevents many VoIP problems from developing and ensures consistent call quality for business communications. Implementing systematic monitoring and maintenance procedures helps identify potential issues before they impact users.
Monitoring and Maintenance Strategies
Network performance monitoring provides early warning of developing problems that could affect VoIP call quality. Implement monitoring systems that track bandwidth utilization, latency, jitter, and packet loss on a continuous basis. Network infrastructure plays a crucial role in VoIP performance, and proactive maintenance prevents many common issues.
Regular configuration backups ensure that you can quickly restore working network settings if problems develop after configuration changes. Schedule automatic backups of router and firewall configurations, and test restoration procedures periodically to verify backup integrity.
Staff Training and Documentation
Employee training on proper VoIP usage helps prevent user-caused problems and ensures efficient reporting when issues occur. Train staff on features like hold, transfer, and conference calling to maximize system utilization while minimizing support requirements.
Comprehensive documentation of network configurations, troubleshooting procedures, and vendor contact information enables faster problem resolution when issues develop. Maintain current documentation that includes network diagrams, configuration details, and step-by-step VoIP troubleshooting tips and guides.

Frequently Asked Questions
Will disabling SIP ALG affect other network functions besides VoIP? Disabling SIP ALG typically has no impact on other network functions, as this feature specifically targets SIP traffic. However, if your network relies on other ALG functions for specialized applications, consult with your IT administrator before making changes to ensure no unexpected service disruptions occur.
How can I tell if SIP ALG is causing my VoIP problems? Common symptoms of SIP ALG interference include one-way audio, phones that randomly lose registration, failed call transfers, and calls that connect but have no audio. If you experience these issues consistently and they improve after disabling SIP ALG, this router feature was likely the cause.
Should I contact my VoIP provider before disabling SIP ALG? While not strictly necessary, consulting with your VoIP provider can provide valuable guidance specific to your system configuration. Many providers offer detailed recommendations for SIP ALG router settings and can help verify that your network configuration supports optimal call quality.
What should I do if disabling SIP ALG doesn’t resolve my VoIP issues? If problems persist after disabling SIP ALG, focus on other common VoIP troubleshooting areas, including bandwidth adequacy, QoS configuration, firewall port settings, and network hardware performance. Complex issues may require professional network analysis to identify root causes.
Ensuring Business Continuity with SIP.US
Modern businesses can’t afford communication disruptions that impact customer service and operational efficiency. When you disable SIP ALG for VoIP, you’re taking an important step toward reliable business communications, but comprehensive VoIP success requires partnership with a provider that understands the complexities of modern voice systems.
Common SIP trunk troubleshooting becomes much easier when working with an experienced provider. SIP.US delivers enterprise-grade SIP trunking services designed to work seamlessly with properly configured networks. Our technical team provides expert guidance on network optimization, helping businesses achieve reliable voice communications without the complications introduced by outdated technologies like SIP ALG. Get started with SIP.US today to experience the difference that professional SIP trunking makes for your business communications.



