SIP Trunk Pricing Calculator & Cost Examples
SIP trunk pricing varies significantly based on business size, call volume, and chosen pricing model, making accurate cost estimation essential for smart decision-making.
- Interactive calculators help businesses estimate costs across different pricing models and determine optimal channel requirements
- Most organizations save on communication expenses compared to traditional phone systems when switching to SIP trunking
- Channel requirements typically range from 1 per 3–4 employees for standard businesses, though call centers may need higher ratios
- Hidden costs like bandwidth upgrades and setup fees can significantly impact total investment
Use multiple pricing scenarios and factor in total cost of ownership when evaluating SIP trunk solutions to ensure accurate budgeting and maximum ROI.
The global SIP trunking market shows expansion from $54.20 billion in 2023 to $177.84 billion by 2032. This explosive growth reflects businesses’ urgent need for cost-effective, scalable communication solutions that can support modern work environments while delivering significant savings over traditional phone systems.
Understanding SIP trunk pricing has become essential for organizations seeking to modernize their communications infrastructure. With multiple pricing models available and varying cost factors to consider, businesses need reliable tools and examples to make informed decisions. This comprehensive guide helps you navigate SIP trunk pricing and find the solution that best fits your budget and requirements.
How Does SIP Trunk Pricing Work?
SIP trunk pricing operates differently from traditional phone systems, offering businesses more flexibility and control over their communication costs. Unlike conventional phone lines that require physical infrastructure and fixed-line rentals, SIP trunks utilize internet connectivity, which can dramatically reduce ongoing expenses while providing enhanced features and scalability.
The fundamental principle behind SIP trunk pricing revolves around virtual channels rather than physical lines. Each channel represents the ability to handle one concurrent call, either inbound or outbound. Businesses can purchase exactly the capacity they need without paying for unused lines, making it a more cost-effective solution for organizations with varying call volumes.
Most providers structure their SIP trunk costs around several key components. The primary expense typically involves monthly fees based on the number of channels required, with additional charges for phone numbers (DIDs) and enhanced features. Setup fees may apply for initial configuration, though many modern providers have eliminated these charges to remain competitive.
Understanding the relationship between channels and actual usage patterns is essential for accurate pricing estimation. Most businesses require approximately one channel for every 3–4 employees, though this ratio can vary based on industry, call patterns, and business model. Call centers and sales organizations typically need higher ratios, while office-based businesses with moderate phone usage can often operate efficiently with fewer channels.
Understanding what SIP trunks are and how they function helps businesses make more informed decisions about channel requirements and pricing models.
SIP Trunk Pricing Models Explained
Metered Pricing Models
Metered pricing operates on a pay-per-use basis, charging businesses for actual call minutes consumed. Rates vary by provider and destination. Metered pricing works well for businesses with unpredictable call volumes or seasonal fluctuations, as costs directly correlate with usage.
The primary advantage of metered pricing is its flexibility and transparency. Organizations only pay for calls they actually make, making it ideal for startups, consulting firms, or businesses with light phone usage. However, costs can become unpredictable during high-volume periods, making budgeting more challenging for finance teams.
Unmetered Pricing Models
Unmetered pricing offers unlimited calling for a fixed monthly fee per channel, with costs varying based on the provider and included features. This model provides predictable billing and easier budget management, making it popular among businesses with high call volumes or extensive customer service operations.
Research indicates that businesses can save up to 75% on telecommunication costs when switching from traditional phone systems to SIP trunking with unlimited plans. This model works particularly well for organizations making frequent long-distance calls, where per-minute charges would otherwise accumulate quickly.
Per-Channel Pricing
Per-channel pricing focuses on the number of simultaneous call paths required rather than minutes used. Each channel allows one concurrent call, and businesses pay a monthly fee based on their total channel count. This model provides excellent scalability, as channels can be added or removed as business needs change without requiring physical infrastructure modifications.
The channel-based approach aligns well with business growth patterns, allowing organizations to scale their communication capacity alongside their workforce expansion. Most providers offer flexible channel management through online portals, enabling real-time adjustments based on changing requirements.
Block Pricing
Block pricing involves purchasing predetermined bundles of minutes at discounted rates, such as 1,000 or 5,000 minutes per month. This model offers a middle ground between metered and unlimited pricing, providing cost savings for medium-volume users while maintaining some usage predictability.
Organizations can often negotiate better block pricing rates based on their historical usage patterns and growth projections. Unused minutes may roll over to subsequent months or expire, depending on the provider’s terms and conditions.
Cost Examples by Business Size
Small Business (5–25 Employees)
Small businesses typically require fewer channels depending on their industry and call patterns. For example, a professional services firm with 15 employees might need approximately four channels for normal operations. Additional expenses include DID numbers and enhanced features like call recording or auto-attendant, with costs varying by provider and feature set.
Monthly costs for small businesses vary widely based on requirements and provider selection but generally represent significant savings compared to traditional phone systems. Research indicates that VoIP services, including SIP trunking, are projected to grow from $167.3 billion in 2024 to $752.41 billion by 2034, demonstrating the widespread adoption of these cost-effective solutions.
Medium Business (25–100 Employees)
Medium-sized organizations require more complex configurations with additional channels to handle their communication needs. For example, a manufacturing company with 60 employees might deploy 15 channels across multiple departments, with costs varying based on provider and feature requirements.
These businesses often benefit from volume discounts and enhanced support services, with total SIP trunk costs including additional features like conference bridging, call analytics, and disaster recovery capabilities. The ROI typically materializes within the first year due to eliminated hardware costs and reduced maintenance requirements.
Enterprise Business (100+ Employees)
Large enterprises with distributed workforces require sophisticated SIP trunk deployments spanning multiple locations and departments. Organizations with hundreds of employees typically need substantial channel capacity, with costs varying based on global calling requirements and integration complexity.
Enterprise SIP trunk implementations often involve significant monthly investments, but annual savings compared to traditional systems can be substantial. These organizations frequently negotiate custom pricing arrangements and benefit from dedicated support teams and advanced analytics platforms.
What Factors Affect SIP Trunk Costs?
Call Volume and Pattern Analysis
Call volume represents one of the most significant factors influencing SIP trunk pricing decisions. Organizations must analyze both average and peak calling periods to determine appropriate channel counts and pricing models. Businesses with predictable calling patterns benefit from unlimited plans, while those with sporadic usage may prefer metered options.
Seasonal businesses face unique challenges in SIP trunk planning, as their channel requirements may fluctuate dramatically throughout the year. Retailers experiencing holiday surges or tax preparation services handling seasonal volumes need flexible pricing arrangements that accommodate these variations without penalty fees.
Geographic and International Requirements
Geographic scope significantly impacts SIP trunk costs, particularly for organizations with international operations or customer bases. Domestic calling within the US48 and Canada is typically included in standard pricing, while international destinations carry additional per-minute charges that vary by country and carrier agreements.
Businesses with global operations often negotiate custom international calling packages or establish local SIP trunk presence in key markets to minimize international charges. This approach can reduce costs while improving call quality for international communications.
Feature and Integration Requirements
Advanced features like call recording, analytics, CRM integration, and disaster recovery capabilities add to base SIP trunk costs but often provide substantial value through improved productivity and compliance capabilities. Organizations must balance feature costs against operational benefits when designing their SIP trunking solutions.
Integration with existing business applications, particularly Microsoft Teams, often requires specialized configuration and may involve additional licensing fees. However, these integrations typically deliver significant productivity improvements that justify the additional investment.
Infrastructure and Bandwidth Considerations
SIP trunk calls require approximately 85–100 kilobits per second of bandwidth per concurrent call, making internet infrastructure a critical cost factor. Organizations with limited bandwidth may need to upgrade their connections, adding monthly costs but improving overall communication quality and reliability.
Quality of Service (QoS) implementation becomes essential for businesses making high volumes of concurrent calls. While QoS configuration may require professional services, it ensures consistent call quality and prevents communication disruptions during peak usage periods.
5 Hidden Costs That Impact Your SIP Trunk Budget
1. Bandwidth Upgrades and Network Infrastructure
Many organizations underestimate the internet infrastructure requirements for successful SIP trunk deployment. Each concurrent call consumes approximately 85kbps of bandwidth, meaning businesses must ensure adequate upload speeds to maintain call quality during peak periods.
Network upgrades often involve monthly recurring charges for increased bandwidth, potential equipment purchases for QoS implementation, and professional services for network optimization. These costs can vary depending on current infrastructure and required improvements.
2. Equipment and Hardware Requirements
While SIP trunks eliminate many traditional phone system hardware requirements, businesses may still need to invest in IP-enabled handsets, session border controllers, or PBX upgrades. Organizations transitioning from analog systems face higher equipment costs than those already using IP-based communications.
Equipment costs vary based on quality and features required, but these one-time expenses often pay for themselves through reduced maintenance and improved functionality compared to legacy systems.
3. Emergency Services and Compliance
Enhanced 911 (E911) services are mandatory for business phone systems, adding monthly fees per DID number. E911 ensures emergency responders can automatically locate callers, but implementation requires careful address management and may involve additional setup charges.
Compliance requirements vary by industry, with healthcare and financial services organizations facing additional costs for call recording, encryption, and audit trail capabilities. These features add to monthly costs but are essential for regulatory compliance.
4. Toll-Free and Premium Calling
Premium numbers and certain toll-free destinations may carry surcharges not included in standard pricing. Organizations should review their historical calling patterns and establish appropriate restrictions or budgets for these services.
5. Support and Professional Services
Implementation and ongoing support costs vary among providers, with some including basic support in monthly fees while others charge separately for advanced technical assistance. Professional services for complex deployments can vary widely depending on requirements and scope.
Consider budgeting for initial configuration assistance, training for administrative staff, and ongoing support during the first year of operation. These investments ensure smooth deployment and optimal utilization of SIP trunk features.
How to Estimate Your SIP Trunk Needs
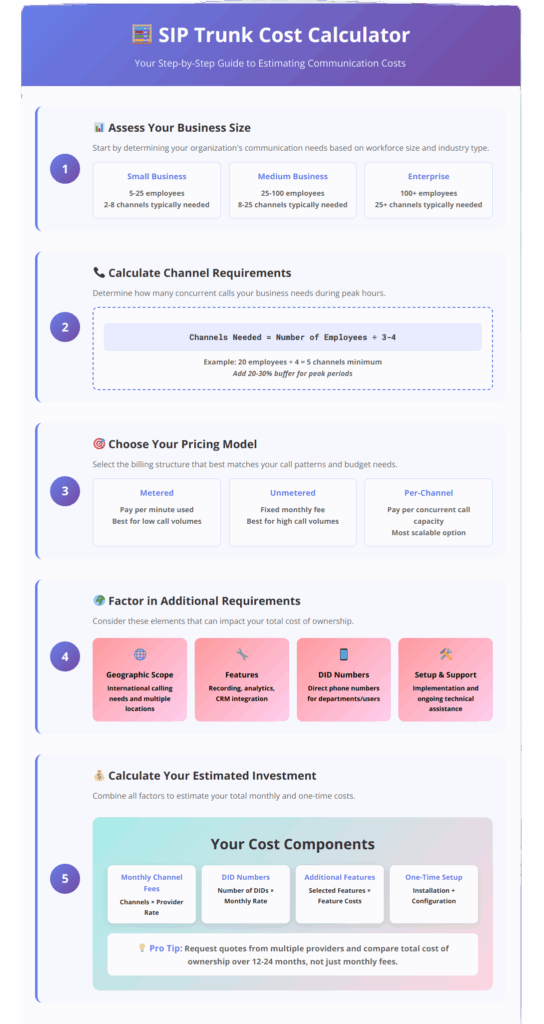
Channel Calculation Methods
Accurate channel estimation requires analyzing historical call data and peak usage patterns. The Erlang B formula provides a mathematical approach to calculating required channels based on call volume and acceptable blocking probability, though most businesses can use simpler estimation methods for initial planning.
Start by monitoring current phone usage during the busiest hour of your typical business day. Count the maximum number of simultaneous calls and add a 20–30% buffer for growth and unexpected peaks. This approach provides a practical starting point for channel requirements while avoiding over-provisioning.
Growth Planning and Scalability
SIP trunk planning should accommodate business growth projections over 2–3 years to avoid frequent reconfigurations. Consider factors like planned hiring, new office locations, seasonal variations, and potential changes in business model that might affect communication requirements.
Build growth assumptions into your initial channel estimates, as adding capacity later is easier and more cost-effective than over-provisioning initially. Most providers offer flexible channel management, allowing adjustments as actual usage patterns become clear.
Peak Usage Analysis
Identify your organization’s peak calling periods and ensure adequate channel capacity during these times. Many businesses experience predictable peaks during specific hours, days of the week, or seasons that require careful planning to maintain service quality.
Document peak usage patterns over several months to establish baseline requirements. Consider external factors like marketing campaigns, product launches, or industry events that might temporarily increase call volumes beyond normal patterns.



